Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, playing a vital role in the way we perceive and interact with the world around us. From the smallest atoms to the largest galaxies, electromagnetism governs much of the behavior of matter.

What is Electromagnetism?
Electromagnetism is the area of
physics which tries to represent how electricity and magnetism relate together.
On the most fundamental level, it's a question of how electric charges give
rise to magnetic fields and how these fields behave toward other charges. The
theory of electromagnetism is based on a group of laws collectively known as Maxwell's
equations, which were first presented by Scottish physicist James Clerk
Maxwell during the 19th century.
Key Factors of Electromagnetism:
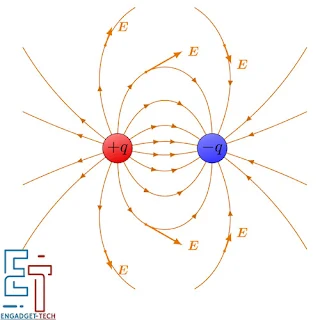
1. Electric Fields:
It is a space region through
which an electric charge exerts a force. These fields come due to electric
charges and affect other charges, and these are nearby ones. The strength of
the electric field is proportional to the amount of charge which generates it
and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the charge.
2. Magnetic Fields:
Magnetic field is that field in
which force is experienced by moving electric charges or magnetic materials
like iron. Magnetic fields are always produced by moving charges (current), and
they are closely related to electric fields. Indeed, changing an electric field
leads to a production of magnetic field and vice versa.

3. Electromagnetic Force:
The electromagnetic force is the
effect both by the electric fields and magnetic fields. It further defines the
attraction or repulsion of charged particles, behavior in electrical circuits,
and also the production of light.

4. Maxwell's Equations:
These are four basic equations
that define the behavior of electric and magnetic fields. They consist of
Gauss's Law for Electricity: This law
describes the way electric charges form electric fields.
Gauss's Law for Magnetism: Magnetic
field lines have no beginning or end; they are closed loops.
Faraday's Law of Induction: A
changing magnetic field can induce a changing electric current.
Ampere's Law (with Maxwell's
correction): It describes how the strength of the magnetic
field is generated from sources that created it, by electric current and the
rate of change of the electric field.

Electromagnetic Technology
Advancement:
Electromagnetic technology is an
area where some significant advancements have been recorded in the recent past.
Some of the emerging technologies in this field are:
Wireless Power Transfer
Electromagnetic induction into
the development of wireless charging for devices such as smartphones and
electric cars is also developing new ways to power further wirelessly at
greater distances.
Quantum Electrodynamics (QED)
QED represents the quantum field
theory through which one can describe the interaction of light with matter. QED
furnished deep insights into the nature of electromagnetism at the quantum
level, and it was found to be applied in particle physics and in application
development, such as lasers.
Electromagnetic Suspension
One of the most celebrated examples
is in the maglev train where super powerful magnetic fields suspend and propel
trains along a track at super-high speeds that provide little friction and
therefore minimal loss of energy to resistance, as the train doesn't touch the
tracks.
High Temperature Superconductors
They are found in the most
advanced scientific application in other words particle accelerators and fusion
reactors. The strongest magnetic fields without energy loss because of
resistance are formed by high-temperature superconductors.
Conclusion:
One of the most fundamental
forces of nature, electromagnetism shapes most aspects of the world from the
behavior of atoms to complex systems of technology, transforming society
because it enables generations of change in power, communication, medical
imaging, transportation, and data storage.
Such knowledge of
electromagnetism adds to the knowledge we have of the universe and provides a
route for future technological innovation. Emergent research into
electromagnetic fields and waves has created new breakthroughs leading to the
creation of tomorrow's technology.



.jpg)





0 Comments